Value Objects?
Value Objects represent descriptive aspects of the domain that do not possess a unique identity. Instead, they are defined entirely by their attributes. If two value objects have the same attribute values, they are considered equal.
Several examples already exist the workshop codebase. For example
ts
There are a couple of things going on here.
TypeORM
We’re using TypeORM as our Object Relational Mapping (ORM) tool. These @Column decorators indicate that each of these class fields should be persisted in a database (in this case a SQLite DB at packages/server/peashoot.sqlite)
The @peashoot/types package
This app has a client-server architecture, and @peashoot/types is where we’re storing a very specific set of things
- Common types for request/response shapes -
packages/types/src/resources/* - Common types that are included in those request/response shapes -
packages/types/src/entities/* - Some type guards and utility functions that go along with those types
In this package we use Zod schemas which look like this
ts
Entities
In DDD, Entities as persisted, mutable objects. In our app, this means they’ll have IDs and will each relate to a table in our database. There’s a relevant example in our app already
ts
the base class PeashootEntity<'loc'> takes care of the id field for us, and prefixes it with loc_ so that they’re easy to identify if we ever see them logged.
The @Entity decorator is really important here. This is what means these are persisted in a table (as opposed to the value-objects which are embedded in the tables of entities they belong to)
Our task
Our app contains a calculator UI
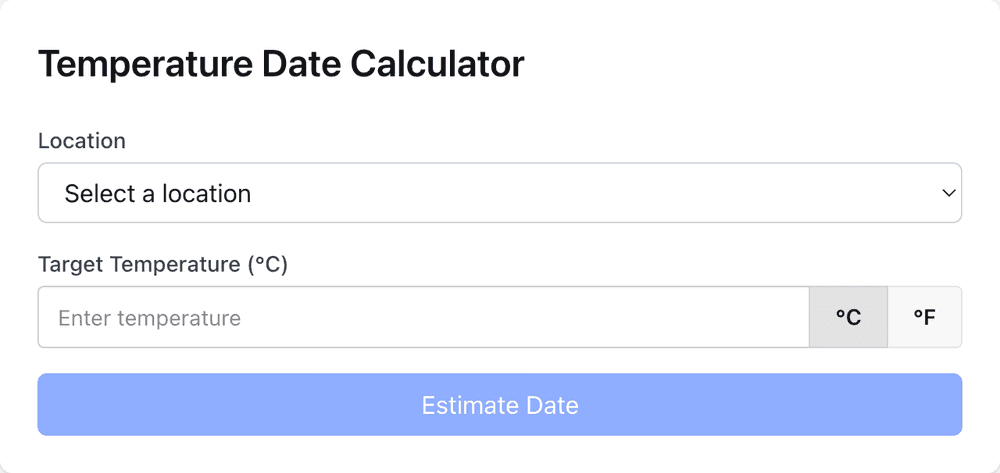 where a gardener can enter a location and temperature, and they need to be able to get an estimate of the date when the weather will be no colder than that temperature.
where a gardener can enter a location and temperature, and they need to be able to get an estimate of the date when the weather will be no colder than that temperature.
Here’s how the data flow works
- The UI component is
packages/client/src/pages/CalculatorsPage.svelte - The request initiates from the client at
packages/client/src/lib/repositories/location-temperature-data.repository.tsin thecalculateDatemethod - The request/response shapes are described here
packages/types/src/resources/locations-calculate-date.ts - And ultimately the location service is
packages/server/src/services/location.tswhich makes the calculation and returns a date, which bubbles back up to the UI. You may notice that there’s a data file being read and we’re not doing anything with it yet (perhaps we should?)
We have a very basic model for Location here
packages/server/src/entities/location.ts — but we’ll need to do more in order to complete this task.
Before you begin
Think about value objects and entities? Can we draw a simple diagram of what we plant to build?